Given a binary tree root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
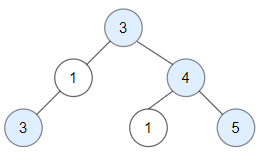
Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5] Output: 4 Explanation: Nodes in blue are good. Root Node (3) is always a good node. Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root. Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
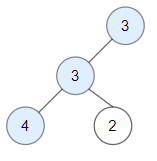
Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2] Output: 3 Explanation: Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because "3" is higher than it.
Input: root = [1] Output: 1 Explanation: Root is considered as good.
- The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
[1, 10^5]. - Each node's value is between
[-10^4, 10^4].
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def goodNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def foo(root: TreeNode, max_val: int) -> int:
max_val = max(max_val, root.val)
ret = 1 if root.val >= max_val else 0
ret += foo(root.left, max_val) if root.left else 0
ret += foo(root.right, max_val) if root.right else 0
return ret
return foo(root, -10000)