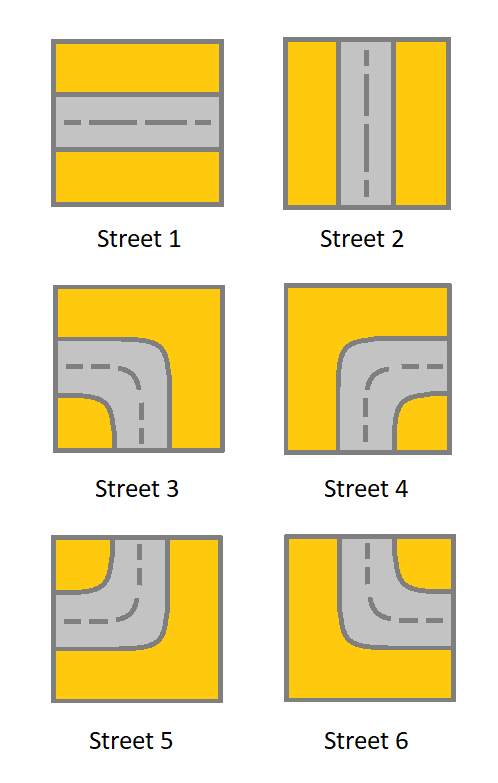
You are given an m x n grid. Each cell of grid represents a street. The street of grid[i][j] can be:
1which means a street connecting the left cell and the right cell.2which means a street connecting the upper cell and the lower cell.3which means a street connecting the left cell and the lower cell.4which means a street connecting the right cell and the lower cell.5which means a street connecting the left cell and the upper cell.6which means a street connecting the right cell and the upper cell.
You will initially start at the street of the upper-left cell (0, 0). A valid path in the grid is a path that starts from the upper left cell (0, 0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1). The path should only follow the streets.
Notice that you are not allowed to change any street.
Return true if there is a valid path in the grid or false otherwise.
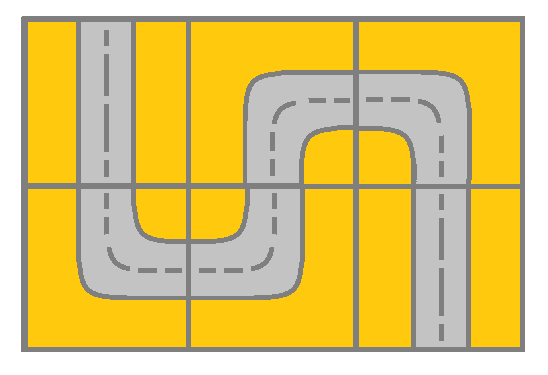
Input: grid = [[2,4,3],[6,5,2]] Output: true Explanation: As shown you can start at cell (0, 0) and visit all the cells of the grid to reach (m - 1, n - 1).
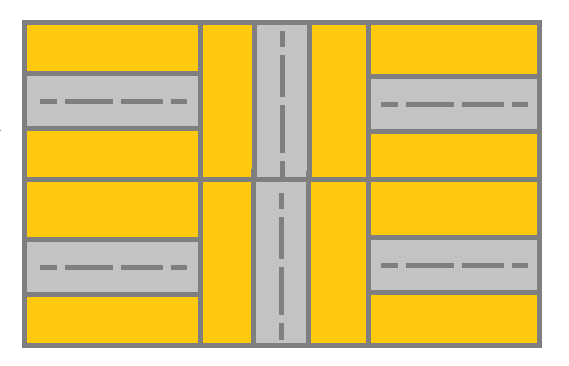
Input: grid = [[1,2,1],[1,2,1]] Output: false Explanation: As shown you the street at cell (0, 0) is not connected with any street of any other cell and you will get stuck at cell (0, 0)
Input: grid = [[1,1,2]] Output: false Explanation: You will get stuck at cell (0, 1) and you cannot reach cell (0, 2).
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3001 <= grid[i][j] <= 6
use std::collections::HashSet;
impl Solution {
pub fn has_valid_path(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut seen = HashSet::new();
let mut cells = vec![(0, 0)];
while let Some((i, j)) = cells.pop() {
if i == m - 1 && j == n - 1 {
return true;
}
seen.insert((i, j));
match grid[i][j] {
1 => {
if j > 0 && !seen.contains(&(i, j - 1)) && [1, 4, 6].contains(&grid[i][j - 1]) {
cells.push((i, j - 1));
}
if j + 1 < n
&& !seen.contains(&(i, j + 1))
&& [1, 3, 5].contains(&grid[i][j + 1])
{
cells.push((i, j + 1));
}
}
2 => {
if i > 0 && !seen.contains(&(i - 1, j)) && [2, 3, 4].contains(&grid[i - 1][j]) {
cells.push((i - 1, j));
}
if i + 1 < m
&& !seen.contains(&(i + 1, j))
&& [2, 5, 6].contains(&grid[i + 1][j])
{
cells.push((i + 1, j));
}
}
3 => {
if j > 0 && !seen.contains(&(i, j - 1)) && [1, 4, 6].contains(&grid[i][j - 1]) {
cells.push((i, j - 1));
}
if i + 1 < m
&& !seen.contains(&(i + 1, j))
&& [2, 5, 6].contains(&grid[i + 1][j])
{
cells.push((i + 1, j));
}
}
4 => {
if j + 1 < n
&& !seen.contains(&(i, j + 1))
&& [1, 3, 5].contains(&grid[i][j + 1])
{
cells.push((i, j + 1));
}
if i + 1 < m
&& !seen.contains(&(i + 1, j))
&& [2, 5, 6].contains(&grid[i + 1][j])
{
cells.push((i + 1, j));
}
}
5 => {
if i > 0 && !seen.contains(&(i - 1, j)) && [2, 3, 4].contains(&grid[i - 1][j]) {
cells.push((i - 1, j));
}
if j > 0 && !seen.contains(&(i, j - 1)) && [1, 4, 6].contains(&grid[i][j - 1]) {
cells.push((i, j - 1));
}
}
_ => {
if i > 0 && !seen.contains(&(i - 1, j)) && [2, 3, 4].contains(&grid[i - 1][j]) {
cells.push((i - 1, j));
}
if j + 1 < n
&& !seen.contains(&(i, j + 1))
&& [1, 3, 5].contains(&grid[i][j + 1])
{
cells.push((i, j + 1));
}
}
}
}
false
}
}