You are given an array books where books[i] = [thicknessi, heighti] indicates the thickness and height of the ith book. You are also given an integer shelfWidth.
We want to place these books in order onto bookcase shelves that have a total width shelfWidth.
We choose some of the books to place on this shelf such that the sum of their thickness is less than or equal to shelfWidth, then build another level of the shelf of the bookcase so that the total height of the bookcase has increased by the maximum height of the books we just put down. We repeat this process until there are no more books to place.
Note that at each step of the above process, the order of the books we place is the same order as the given sequence of books.
- For example, if we have an ordered list of
5books, we might place the first and second book onto the first shelf, the third book on the second shelf, and the fourth and fifth book on the last shelf.
Return the minimum possible height that the total bookshelf can be after placing shelves in this manner.
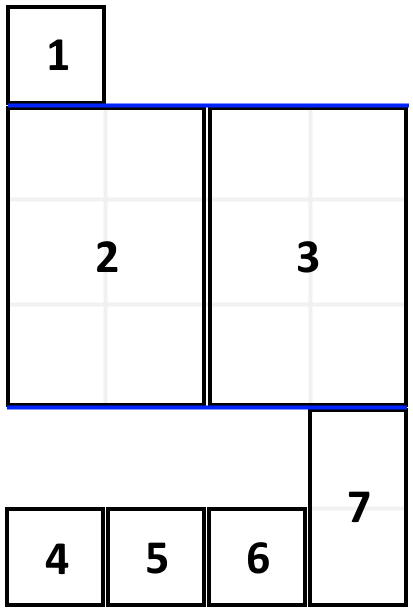
Input: books = [[1,1],[2,3],[2,3],[1,1],[1,1],[1,1],[1,2]], shelfWidth = 4 Output: 6 Explanation: The sum of the heights of the 3 shelves is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6. Notice that book number 2 does not have to be on the first shelf.
Input: books = [[1,3],[2,4],[3,2]], shelfWidth = 6 Output: 4
1 <= books.length <= 10001 <= thicknessi <= shelfWidth <= 10001 <= heighti <= 1000
impl Solution {
pub fn min_height_shelves(books: Vec<Vec<i32>>, shelf_width: i32) -> i32 {
let mut dp = vec![i32::MAX; books.len() + 1];
dp[0] = 0;
for i in 0..dp.len() {
let mut w = 0;
let mut h = 0;
for j in i + 1..dp.len() {
w += books[j - 1][0];
h = h.max(books[j - 1][1]);
if w > shelf_width {
break;
}
dp[j] = dp[j].min(dp[i] + h);
}
}
*dp.last().unwrap()
}
}