Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
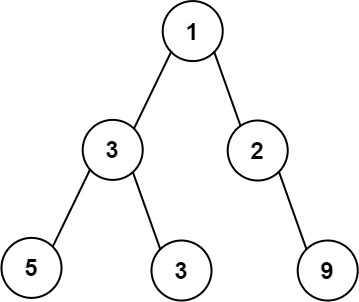
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
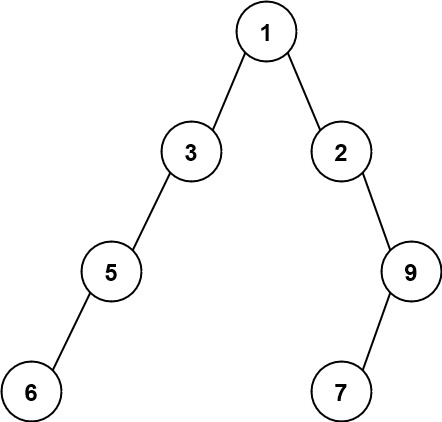
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7] Output: 7 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the fourth level with length 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7).
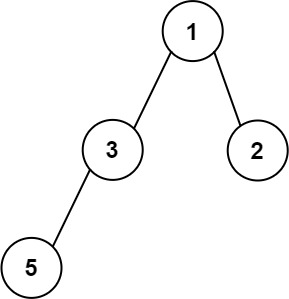
Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the second level with length 2 (3,2).
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
currlevel = [(root, 0)]
ret = 1
while currlevel != []:
nextlevel = []
ret = max(ret, currlevel[-1][1] - currlevel[0][1] + 1)
for node, x in currlevel:
if node.left is not None:
nextlevel.append((node.left, x << 1))
if node.right is not None:
nextlevel.append((node.right, (x << 1) + 1))
currlevel = nextlevel
return ret