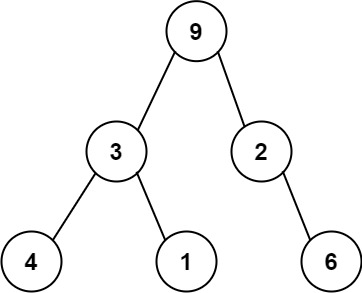
One way to serialize a binary tree is to use preorder traversal. When we encounter a non-null node, we record the node's value. If it is a null node, we record using a sentinel value such as '#'.
For example, the above binary tree can be serialized to the string "9,3,4,#,#,1,#,#,2,#,6,#,#", where '#' represents a null node.
Given a string of comma-separated values preorder, return true if it is a correct preorder traversal serialization of a binary tree.
It is guaranteed that each comma-separated value in the string must be either an integer or a character '#' representing null pointer.
You may assume that the input format is always valid.
- For example, it could never contain two consecutive commas, such as
"1,,3".
Input: preorder = "9,3,4,#,#,1,#,#,2,#,6,#,#" Output: true
Input: preorder = "1,#" Output: false
Input: preorder = "9,#,#,1" Output: false
1 <= preorder.length <= 104preoderconsist of integers in the range[0, 100]and'#'separated by commas','.
Follow up: Find an algorithm without reconstructing the tree.
impl Solution {
pub fn is_valid_serialization(preorder: String) -> bool {
let mut stack = vec![];
for x in preorder.split(',') {
stack.push(x);
while let Some(&[y, "#", "#"]) = stack.get(stack.len() - 3..stack.len()) {
if y == "#" {
break;
} else {
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.push("#");
}
}
}
&stack == &["#"]
}
}