Given an m x n integers matrix, return the length of the longest increasing path in matrix.
From each cell, you can either move in four directions: left, right, up, or down. You may not move diagonally or move outside the boundary (i.e., wrap-around is not allowed).
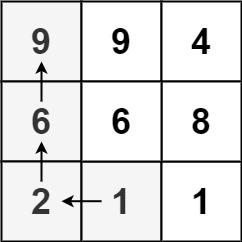
Input: matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest increasing path is [1, 2, 6, 9].
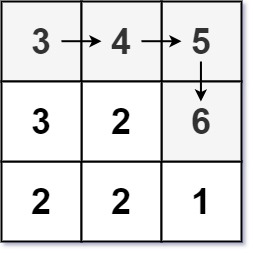
Input: matrix = [[3,4,5],[3,2,6],[2,2,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest increasing path is [3, 4, 5, 6]. Moving diagonally is not allowed.
Input: matrix = [[1]] Output: 1
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
impl Solution {
pub fn longest_increasing_path(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut cells = vec![];
let mut dp = vec![vec![1; n]; m];
let mut ret = 1;
for r in 0..m {
for c in 0..n {
cells.push((r, c));
}
}
cells.sort_unstable_by_key(|&(r, c)| matrix[r][c]);
for (r, c) in cells {
let mut max_path = 0;
if r > 0 && matrix[r - 1][c] < matrix[r][c] {
max_path = max_path.max(dp[r - 1][c]);
}
if r < m - 1 && matrix[r + 1][c] < matrix[r][c] {
max_path = max_path.max(dp[r + 1][c]);
}
if c > 0 && matrix[r][c - 1] < matrix[r][c] {
max_path = max_path.max(dp[r][c - 1]);
}
if c < n - 1 && matrix[r][c + 1] < matrix[r][c] {
max_path = max_path.max(dp[r][c + 1]);
}
dp[r][c] = max_path + 1;
ret = ret.max(dp[r][c]);
}
ret
}
}